YOLO (You Only Look Once) in Computer Vision
Computer Vision
yolo

What Is YOLO?
YOLO is a real-time object detection algorithm that transforms how machines recognize and locate objects in images and video. Traditional object detectors like R-CNN use multiple stages—first generating region proposals, then classifying each region. YOLO simplifies this by combining all steps into a single neural network that directly predicts bounding boxes and class probabilities from the entire image in one evaluation. This approach makes YOLO significantly faster than two-stage detectors, making it ideal for time-sensitive applications such as autonomous driving, video surveillance, and industrial automation.
Key YOLO Versions and Improvements
-
YOLOv1 (2016) introduced the concept of single-stage detection. It divides the input image into a grid and predicts bounding boxes and class probabilities for each cell. This model is fast but struggled with small or overlapping objects.
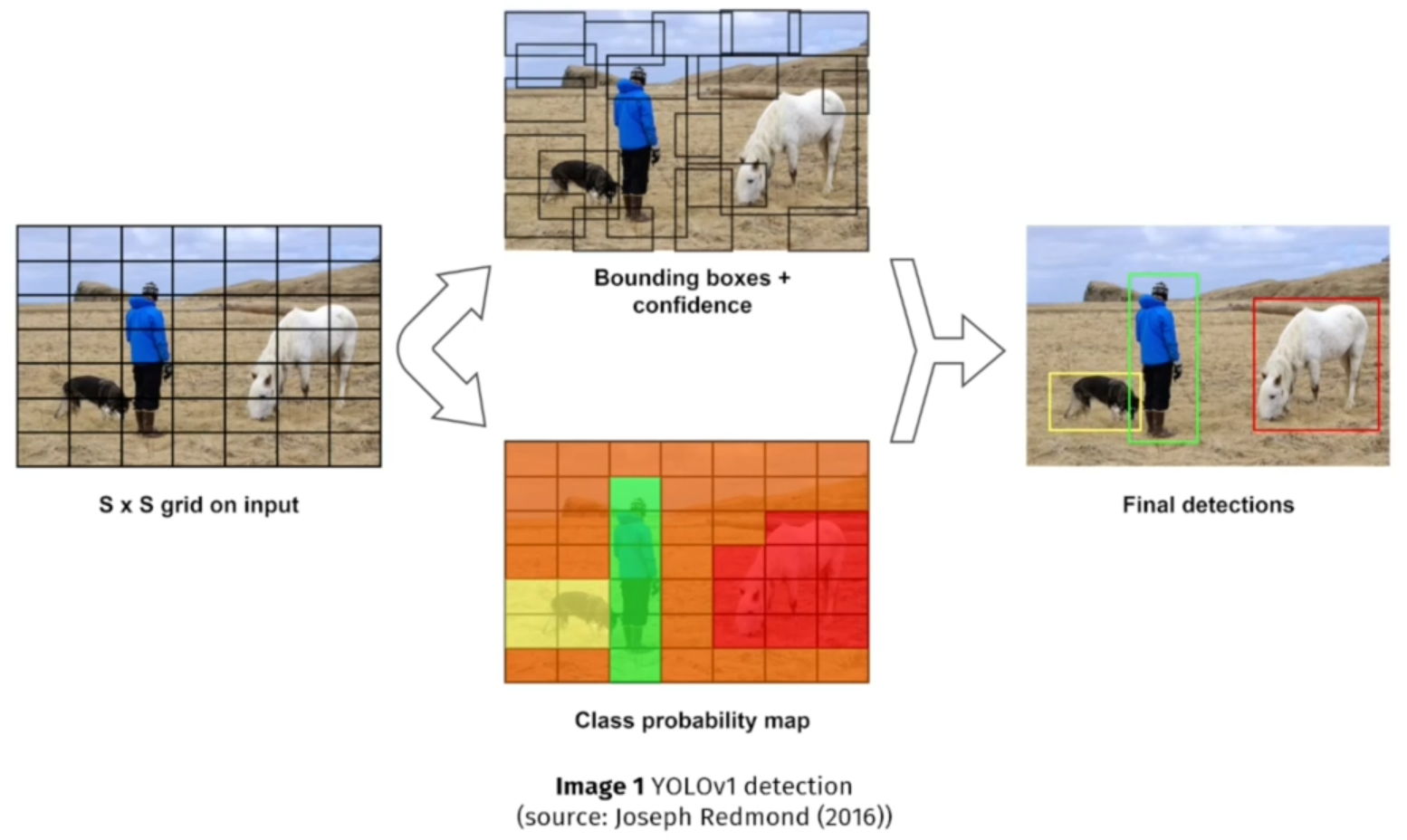
Example: Detecting pedestrians and vehicles in a traffic image for a real-time dashboard in a smart city system.
-
YOLOv2 (YOLO9000) improved detection accuracy and flexibility. It introduced anchor boxes to better predict multiple objects per grid cell and used k-means clustering to select anchor dimensions. It also supported multi-scale training and could detect over 9,000 object categories by combining ImageNet and COCO datasets.
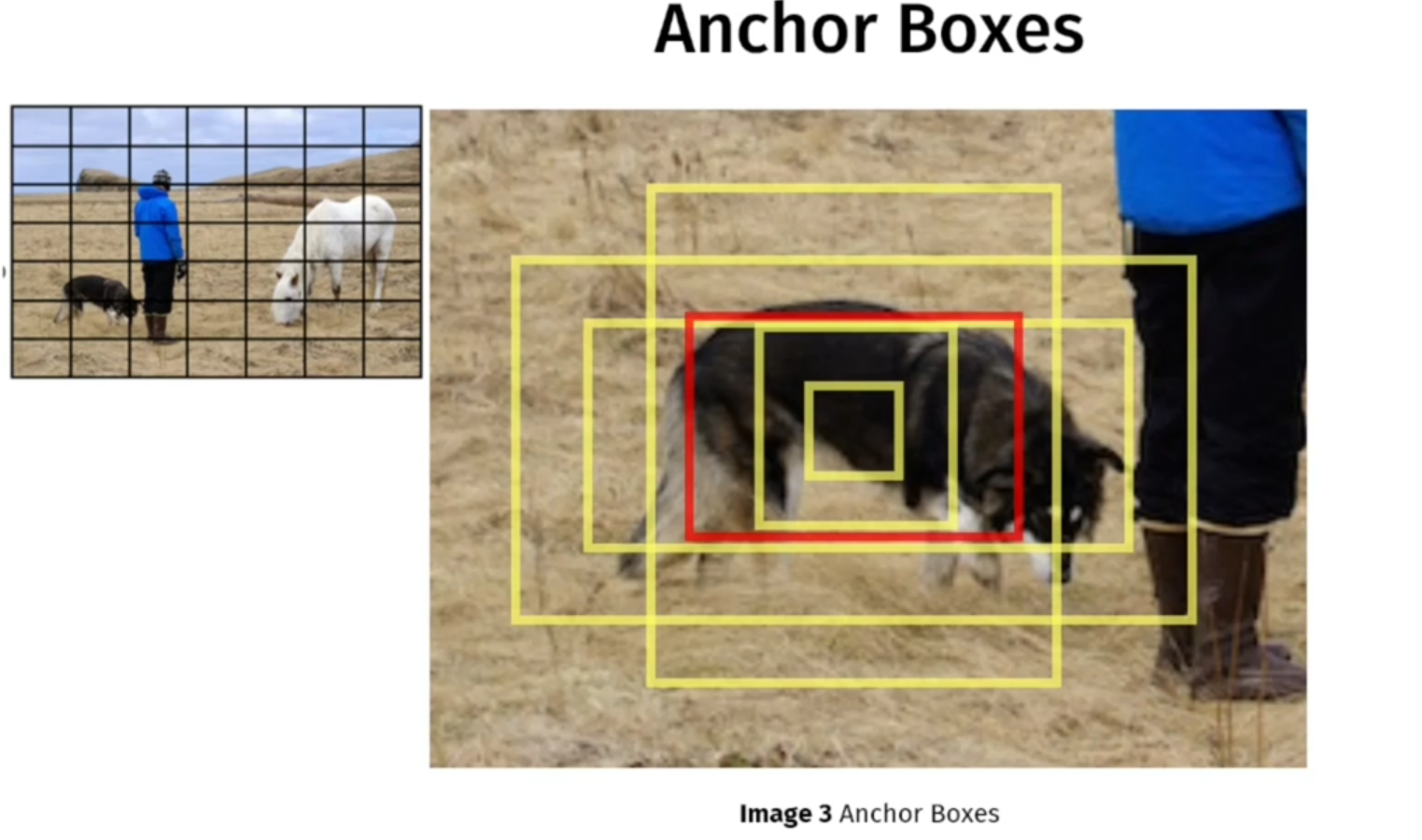
Example: Identifying different species of animals in a crowded wildlife image, even when they are small and close together.
-
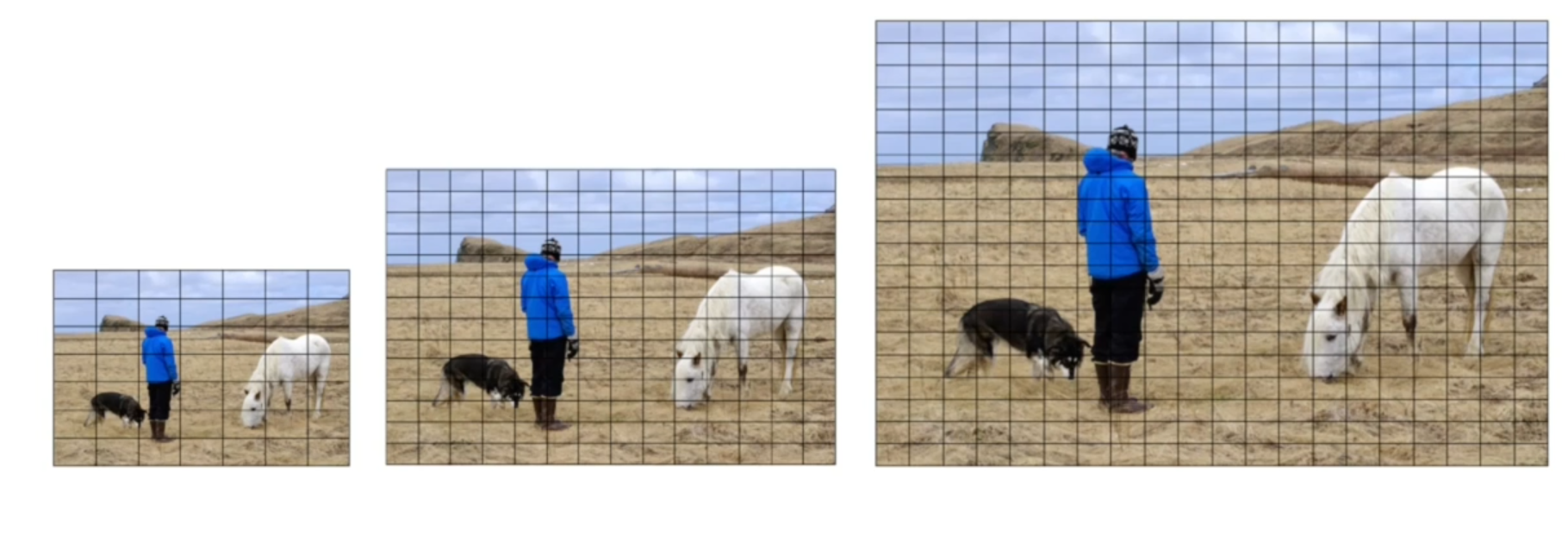
YOLOv3 further enhanced accuracy by using a feature pyramid network (FPN) to predict objects at three different scales—small, medium, and large. It also adopted residual blocks and multi-label classification, improving detection of objects with varying sizes and overlapping features.

Example: Recognizing drones in the sky, cars on the road, and people on sidewalks in one frame of aerial surveillance footage.
-
YOLOv4 (2020) focused on improving both accuracy and speed while remaining accessible to the broader community using conventional GPU hardware.It using Bag of Freebies (BOF) and Bag of Specials (BOS). where BOF is a collection of methods aimed at improving the detection accuracy while lowering inference costs, including data augmentation and regularization techniques. And BOS is a set of menthods that increase a little inference costs while significantly incresing the detection accuracy (e.g. using miss activation function and Cross Stage Partial Connections (CPS)). It also combined techniques like CSPDarknet53 as a backbone, Mish activation, SPP (Spatial Pyramid Pooling), PANet for path aggregation, and various training tricks (e.g., mosaic augmentation, CIoU loss).
Example: Detecting multiple vehicles at different orientations and distances in a real-time traffic monitoring system using mid-range GPUs.
-
YOLOv5 (2020, by Ultralytics) was not released by the original authors but became the most widely used YOLO version due to its ease of use, PyTorch implementation, and active community support. It using Auto Learning Anchor boxes based on the distribution of bounding boxes in the custom dataset with K-means and genetic learning algorithms. This is very important for custom tasks because the distribution of bounding box sizes and locations may be dramatically different compare to Coco dataset.
It introduced automatic mixed precision, improved training speed, and flexible deployment with ONNX, CoreML, and TensorRT export options.
Example: Quickly training a product detection model in a retail checkout system with minimal setup and fast deployment to edge devices.
-
YOLOv6 (by Meituan) aimed at industrial applications. It focused on optimized latency and performance on edge devices. It used Decopled head Architecture that improve its detection, speed and accuracy over its predencessors. It adopted EfficientRep backbone, RepOptimizer, and advanced quantization techniques for deployment in real-world settings.
Example: Real-time detection of manufacturing defects on a production line with low-latency requirements.
-
YOLOv7 (2022) improved accuracy while maintaining real-time performance. It introduced Extended Efficient Layer Aggregation Networks (E-ELAN), model re-parameterization, and better support for both object detection and pose estimation. YOLOv7-Tiny variants were optimized for mobile and embedded use.
It focus using Trainable bag-of-freebies that contains some optimized modules and optimization methods for improving the accuracy that may increase the training cost, but without increasing the inference costs.
Example: Detecting human posture and tools in a warehouse environment using lightweight models on embedded cameras.
-
YOLOv8 (2023, by Ultralytics) added native support for tasks beyond object detection—such as instance segmentation, classification, and pose estimation—within a unified architecture. YOLOv8 models are easier to train and deploy, with improved performance, built-in augmentation, and a modular Python API.
It predicts bounding boxes in the same way that image segmentation does, pixel by pixel by introducing an anchor free detection head methods.
Example: Simultaneously identifying object classes and segmenting them (e.g., separating fish by species and shape) in a single underwater camera feed.
- YOLOv9 introduced two major innovations:
- Programmable Gradient Information (PGI): A technique to preserve input information throughout the network, ensuring reliable gradient flow and improving training efficiency.
- Generalized Efficient Layer Aggregation Network (GELAN): An architecture designed to maximize parameter utilization and computational efficiency, leading to superior performance even in lightweight models.
- YOLOv10 addressed the limitations of Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) by introducing:
- Consistent Dual Assignments: A strategy combining one-to-one and one-to-many label assignments during training, eliminating the need for NMS and reducing inference latency.
- Efficiency-Accuracy Driven Design: Comprehensive optimization of model components to enhance performance while minimizing computational overhead.
- YOLOv11: Enhanced Speed with C3K2 Blocks and Official OBB Support. The final CNN-based iteration, YOLOv11, focused on speed and efficiency by:
- C3K2 Modules: Replacing previous blocks with structures utilizing smaller kernel convolutions, improving feature representation with fewer parameters.
- Depthwise Separable Convolutions: Reducing computational load while maintaining accuracy.
Limitations of YOLOv8 to YOLOv11
Despite these advancements, YOLOv8 through YOLOv11 shared common limitations:
- CNN-Centric Architectures: All models relied heavily on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) without integrating attention mechanisms.
- Lack of Attention Mechanisms: The absence of attention modules limited the models’ ability to capture global context, affecting performance in complex scenes.
But, Attention mechanisms are notoriously resource-intensive, especially when applied to high-resolution inputs. Unlike convolutional operations, which scale linearly with input size, self-attention scales quadratically. For real-time detection tasks, this is a deal-breaker.
Other than that, Attention-based models also suffer from inefficient memory access patterns. During inference, attention maps frequently need to move between the high-speed GPU cache and main memory, slowing things down even more. CNNs, on the other hand, benefit from localized operations and structured memory access, giving them a speed advantage on modern hardware.
- YOLO12: At this architecture, the first time in the series, the YOLO framework shifts from being purely CNN-based to embracing an attention-centric design, all without compromising the real-time performance. With innovations like Area Attention (a more efficient form of local attention), FlashAttention (optimized memory access), and a residual architecture tailored for stability, attention finally becomes viable in real-time detection.
improvement:
- Area Attention: Local Efficiency, Global Awareness. Area Attention splits the input feature map into equal-sized segments along horizontal or vertical directions — usually into 4 parts. Attention is then applied within each of these local “areas.”
- R-ELAN: Making Attention Models Trainable: Residual Efficient Layer Aggregation Network used to improve feature aggregation. The structure in two key ways:
- Residual Connections with Scaling: A shortcut connection is added from the input to the output of each block using a small scaling factor (default = 0.01). This dramatically improves convergence, especially for deep attention-based networks.
- Simplified Aggregation: Instead of splitting and transitioning multiple times like ELAN, R-ELAN:
- Uses a single transition layer to standardize input channels
- Passes through attention/convolutional blocks
- Concatenates only once, reducing memory and compute
- FlashAttention: Fixing the Latency Bottleneck. A custom kernel-level optimization that reduces memory overhead during attention computation. without repeatedly moving data between the GPU cache and main memory.
- MLP Ratio Tweaked: Traditional transformer blocks use a feed-forward network (FFN) with a 4:1 hidden dimension ratio. YOLOv12 reallocates more compute to the attention layers.
- Conv+BN Instead of Linear+LN: Instead of using fully connected layers and layer normalization (common in ViTs), YOLOv12 favors convolution + batch normalization, which improves both performance and GPU efficiency.
- No Positional Embeddings: YOLOv12 removes positional encoding entirely and uses a 7×7 separable convolution (“Position Perceiver”) to inject spatial information in a more lightweight and interpretable way.
- Hierarchical Design Retained: Unlike plain transformer backbones, YOLOv12 keeps the multi-stage, hierarchical structure seen in YOLO model.
The comparison
| Version | Release Year | Backbone / Architecture | Key Features & Improvements | Speed / Performance | Supported Tasks | Typical Use Case Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv1 | 2016 | Custom CNN | Single-stage detector, direct regression, fast but low accuracy on small/overlapping objects | Very fast (real-time) | Object detection | Simple real-time pedestrian detection |
| YOLOv2 | 2017 | Darknet-19 | Anchor boxes, k-means for anchors, multi-scale training, YOLO9000 label integration | Real-time | Object detection (9K+ classes) | Multi-species animal detection in zoo surveillance |
| YOLOv3 | 2018 | Darknet-53 + FPN | Multi-scale detection, residual blocks, better small object detection | Fast, improved accuracy | Object detection (multi-label) | Urban scene analysis from drones (detecting birds, vehicles, people) |
| YOLOv4 | 2020 | CSPDarknet-53 + PANet | Data augmentation (mosaic), SPP, CIoU loss, more trainable tricks | Good speed/accuracy tradeoff | Object detection | Real-time traffic monitoring with mid-tier GPUs |
| YOLOv5 | 2020 (Ultralytics) | Custom PyTorch | Easy deployment (ONNX/TensorRT), auto-augmentation, modular code | Very fast, lightweight | Detection, export-ready deployment | Fast deployment in retail checkout or mobile app object recognition |
| YOLOv6 | 2022 (Meituan) | EfficientRep | Industry-focused, quantization-ready, high FPS at low latency | Optimized for edge | Object detection | Detecting defects in industrial automation settings |
| YOLOv7 | 2022 | E-ELAN + RepConv | Highest accuracy/speed balance, support for pose detection and instance segmentation | SOTA for real-time models | Detection + Pose + Segmentation | Human pose estimation and tool detection in smart warehouses |
| YOLOv8 | 2023 (Ultralytics) | Updated PyTorch | Unified task support (detection, segmentation, classification, pose), simplified API | Modular, best UX | All vision tasks in one model | Instance segmentation + object detection of fish species from underwater video footage |
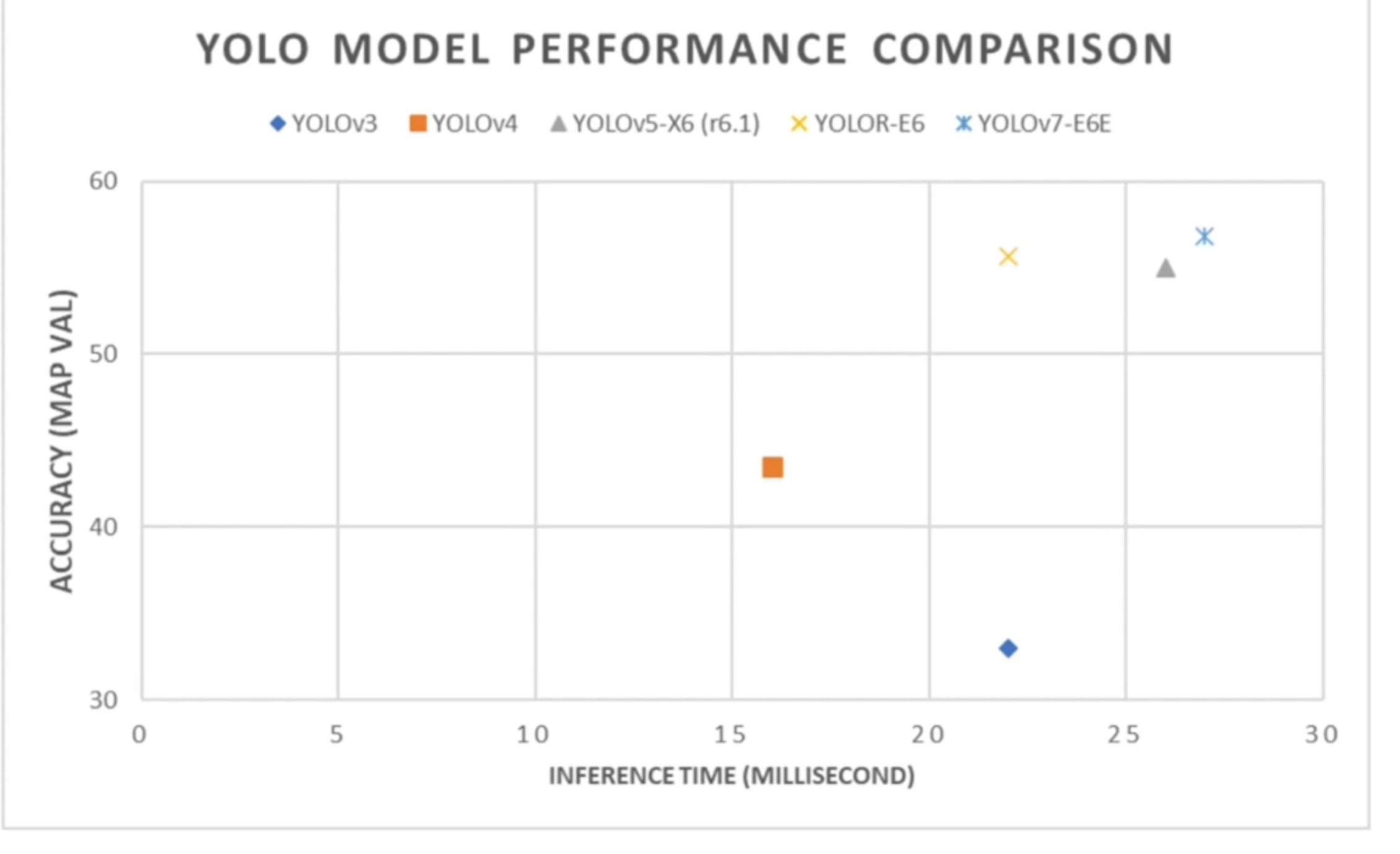
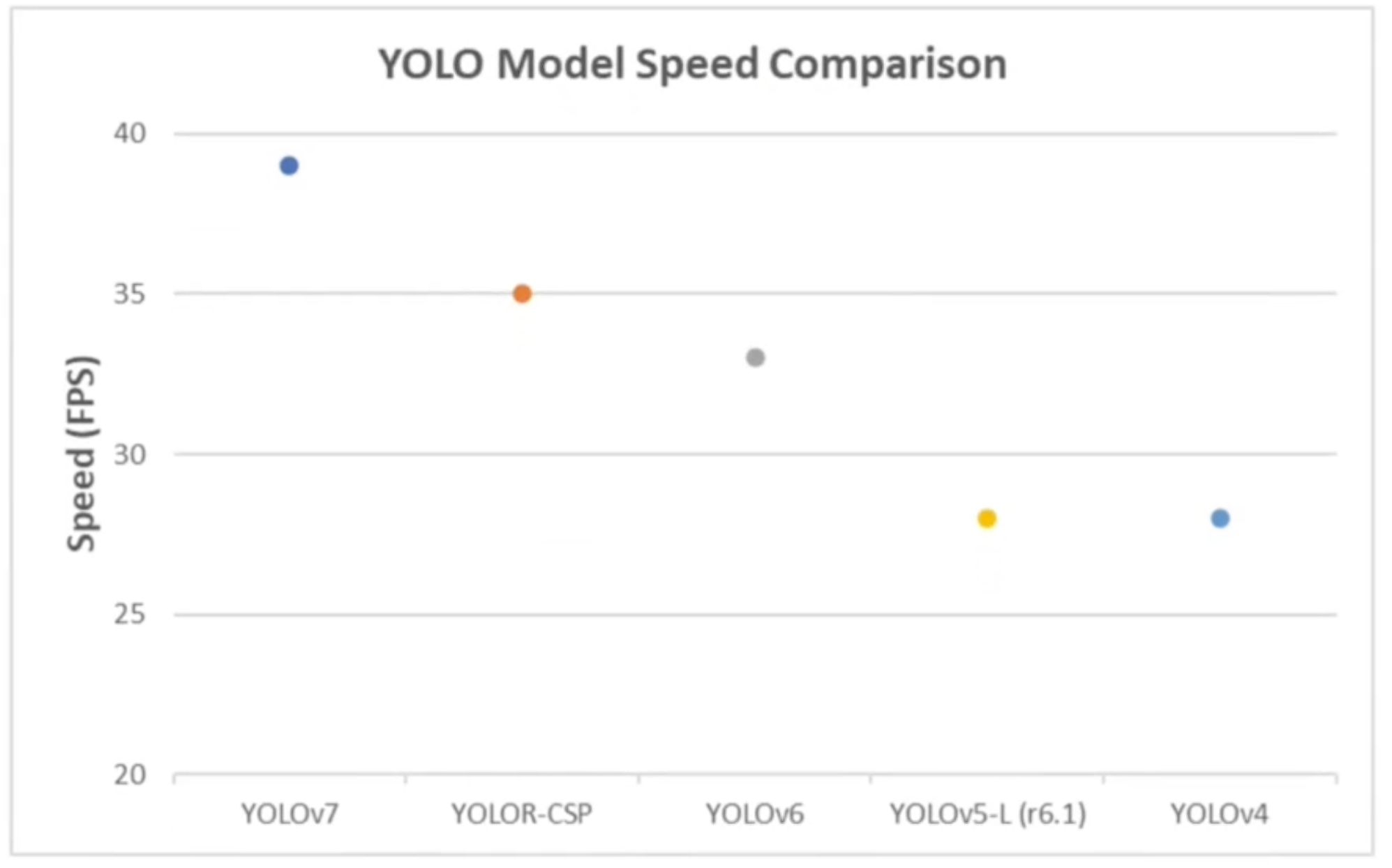
YOLO’s Advantage
- YOLO implements one-stage object detection – Thus, object detection is more rapid whem compared to two stage object detection models.
- YOLO is Open Source – This allows us to distribute, modify and use for commercial purposes.
- The YOLO documentation is extensive, and the forum is very active
- YOLO is frequently updated with new versions and has many variants